Slowloris is without a doubt, one of the favorite attacks of many white/gray/black hats, due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Let's explain quickly graphically what the attack looks like:

Unlike another tutorial about how to test if your server is vulnerable to Slowloris attacks and where we explain how this kind of attack works, this tutorial aims to be a genuine attack, this means one of those attacks that are not limited by some condition in the script, this attack will run forever if you want it (until you close the terminal that runs the attack). We recommend you to read the first article before proceeding with this one.
In this article, we will explain you how to run a Python version of a genuine Slowloris attack in Kali Linux.
1. Clone Slowloris script
Slowloris is basically an HTTP Denial of Service attack that affects threaded servers. It works like this:
- We start making lots of HTTP requests.
- We send headers periodically (every ~15 seconds) to keep the connections open.
- We never close the connection unless the server does so. If the server closes a connection, we create a new one keep doing the same thing.
This exhausts the servers thread pool and the server can't reply to other people. In order to run the attack, we need the logic of slowloris, however we won't write it by ourselves, instead, use the Python Slowloris implementation from an open source repository in Github. Clone the repository with the following command in some directory of your terminal:
Then, switch from directory to the cloned one:
Now inside this directory we will be able to run the attack with the slowloris.py script. For more information about the Python version of the Slowloris script, please visit the official repository at Github here.
2. Performing attack
You will need Python 3.x installed on your Kali Linux system. By default, it comes installed already in Kali Linux, so we will only need to run the slowloris.py script with the following command:
The website URL parameter specifies the website that you want to attack, for example https://mydomain.com. The -s or --sockets parameter specifies the number of sockets that will run simultaneously from the host of the attack. Replacing the values, the command should look something similar to:
By default, the script runs with 150 sockets unless you specify it so, for example with 300 sockets instead:
The output of the attack will be the following one:
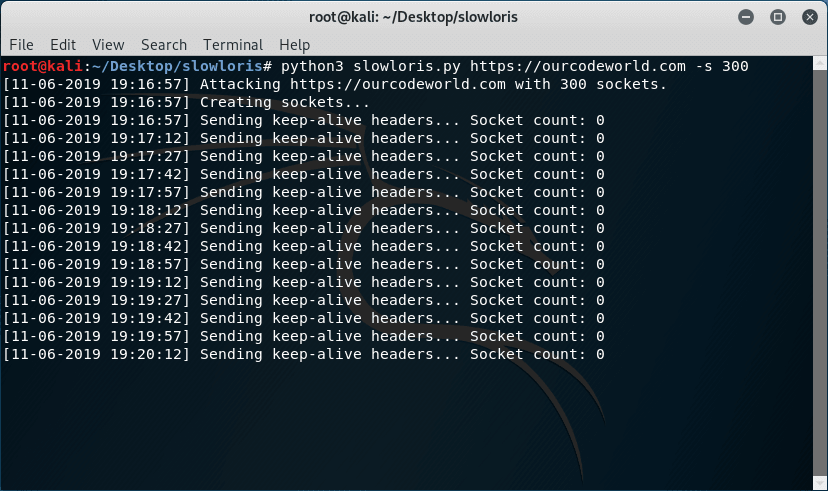
As mentioned, the attack will never end unless you stop it. Remember that you only can run the attack to a website of your property or you will get in serious legal issues.
Happy pentesting !
Comments
Post a Comment