What does "use strict;" means in Javascript
Strict mode makes several changes the way Javascript is handled by the interpreter. Strict mode eliminates some JavaScript silent errors by changing them to throw errors. Strict mode fixes mistakes that make it difficult for JavaScript engines to perform optimizations: strict mode code can sometimes be made to run faster than identical code that's not strict mode and prohibits some syntax likely to be defined in future versions of ECMAScript (i.e classes etc).
Strict mode applies to entire scripts or to individual functions. It doesn't apply to block statements enclosed in {}; attempting to apply it to such contexts doesn't do anything. Basically what use strict does is to introduce better error-checking into your code.
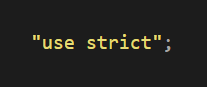
Strict mode can be enabled adding a string with the following content on top of your script "use strict"; i.e :
On a script tag or referenced file :
On function (anonymous or not anonymous)
Prevent duplicates in an object
The following object have 2 properties with the same name:
Without strict mode, the object will have the property but with the latest declared value. Withstrict mode, the js interpreter will throw Uncaught SyntaxError: Duplicate data property in object literal not allowed in strict mode.
Use of with statement disallowed
The use of the with statement in strict mode :
Will throw Uncaught SyntaxError: Strict mode code may not include a with statement. Use of the with statement is not recommended, as it may be the source of confusing bugs and compatibility issues.
Prevents Global Variable Declaration
The declaration of a global variable within a scope is disallowed, for example:
The previous code would throw Uncaught ReferenceError: toSaveInHistory is not definedbecause indeed toSaveInHistory is not declared in the closure. Strict mode forbids implicit creation of global property.
Prevents the use of a reserved keyword as a variable name
The use of a future reserved word for an identifier is invalid. The identifier name is reserved in strict mode , i.e:
- implements
- interface
- package
- private
- protected
- public
- static
- yield
Arguments as an identifier or modify Arguments variable
With strict mode, the variable "arguments" (which is identified as an array in all function, this variable contains all the arguments that were sent to the execution of the function, read more about how argument variable works here) cannot be used as an identifier (variable or function name, parameter name, and so on) nor change the values of members of the local arguments object, i.e:
Variable declared inside an eval function
If a variable is declared inside an eval function, it cannot be used outside that function, i.e :
The previous code throws 'myVariable' is undefined.
Forbids octal syntax
Assigning an octal value to a numeric literal, or attempting to use an escape on an octal value is disallowed, i.e :
The previous code throws Octal numeric literals and escape characters not allowed in strict mode.
Extending a non-extensible object property
Without strict mode, many things are silently ignore, as add a property to a non extensible object will make nothing. But if strict mode is enabled, you'll get an exception i.e :
The previous code throws Cannot create property for a non-extensible object.
Supported browsers
Currently use strict is supported by all major browsers (excluding IE 9 and below). For more information see Can i use use strict. However there are many places in the web where they'll tell that is not a problem to use strict mode in ie8 or 9, if you still doubt, just trust microsoft :
Comments
Post a Comment