ScanSSH is a free and open source utility that scans the given list of addresses or networks for open proxies, SSH protocol servers, Web and SMTP servers. It not just scans, but also displays the version of the running services. You can use it to collect statistics on the deployment of SSH protocol servers in your company or the Internet as whole. You can also use it to ensure all your machines are running the latest SSH protocol versions. The common use case of this utility could be information gathering for the pentesters and security professionals. In this guide, we will see how to install ScanSSH on various Unix-like operating systems and how to use it for gathering details of running services.
Install ScanSSH
On Arch Linux and derivatives, you can install it from AUR using any AUR helper programs such as Yay.
On Fedora:
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
On other distributions, you can download the source from the GitHub page given at the end of this guide and manually compile and install it yourself.
ScanSSH Usage
The typical syntax of ScanSSH is:
Let us see some examples. The following command will scan for ssh servers in a network:
If you want to scan for SSH servers on port 22 only, you could use:
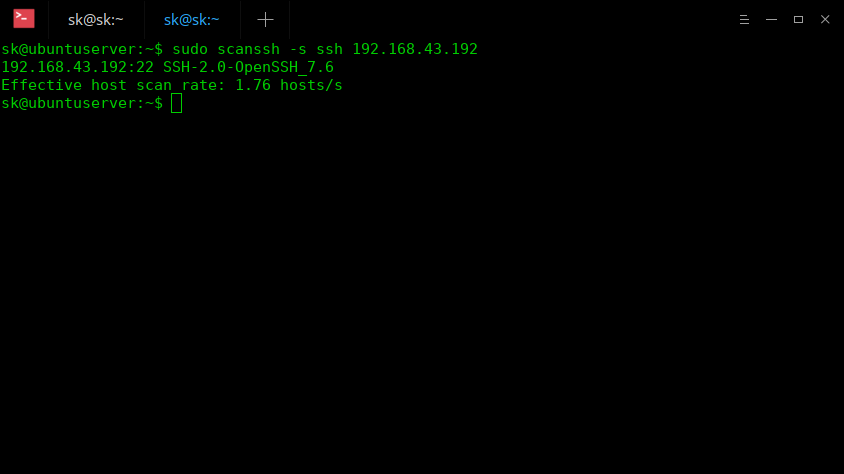
Also, you can specify only one host IP address to scan like below:
And, this command will scan the given network for open proxies.
Here, -p flag is used for scanning open proxies.
Not just SSH and open proxies, ScanSSH will scan for the following modules.
- socks5 – detects SOCKS v5 proxy
- socks4 – detects SOCKS v4 proxy
- http-proxy – detects HTTP get proxy
- http-connect – detects HTTP connect proxy
- telnet-proxy – detects telnet proxy
For more details, check man pages.

Comments
Post a Comment