If you have used MongoDB, you probably have noticed that it follows a default disk usage policy a bit like "take what you can, give nothing back." Here's a simple example: Let's say you have 10 GB of data in a MongoDB database, and you delete 3 GB of that data. However, even though that data is deleted and your database is holding only 7 GB worth of data, that unused 3 GB will not be released to the OS. MongoDB will keep holding on to the entire 10 GB disk space it had before, so it can use that same space to accommodate new data. You can easily see this yourself by running a db.stats():
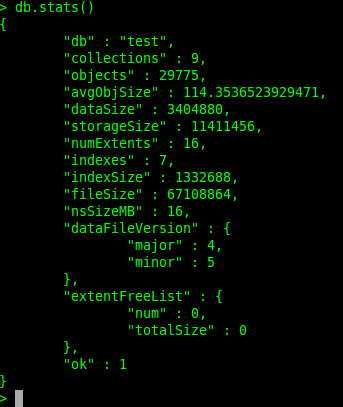
The dataSize parameter shows the size of the data in the database, while storageSize shows the size of data plus unused/freed space. The fileSize parameter, which is essentially the space your database is taking up on disk, includes the size of data, indexes, and unused/freed space.
MongoDB is commonly used to store large quantities of data, often in read-heavy situations where the amount of data manipulation operations are relatively much less. In this kind of situation, it makes sense to anticipate that if you had to handle a certain amount of data before, then you might have to handle a similar amount again. Nevertheless, there will be situations (your development environment, for example) where you don't want to allow MongoDB to keep hogging all your disk space to itself. So, how would you reclaim this disk space? Depending on your setup and the storage engine you're using for your MongoDB, you have a couple of choices.
Compact
The compact command works at the collection level, so each collection in your database will have to be compacted one by one. This completely rewrites the data and indexes to remove fragmentation. In addition, if your storage engine is WiredTiger, the compact command will also release unused disk space back to the system. You're out of luck if your storage engine is the older MMAPv1 though; it will still rewrite the collection, but it will not release the unused disk space. Running the compact command places a block on all other operations at the database level, so you have to plan for some downtime.
Usage example:
Repair
If your storage engine is MMAPv1, this is your way forward. The repairDatabase command is used for checking and repairing errors and inconsistencies in your data. It performs a rewrite of your data, freeing up any unused disk space along with it. Like compact, it will block all other operations on your database. Running repairDatabase can take a lot of time depending on the amount of data in your db, and it will also completely remove any corrupted data it finds.
RepairDatabase needs free space equivalent to the data in your database and an additional 2GB more. It can be run either from the system shell or from within the mongo shell. Depending on the amount of data you have, it may be necessary to assign a sperate volume for this using the --repairpath option.
Usage examples
In the system shell
In the mongo shell
In the mongo shell, with runCommand
Resync
In a replica set, unused disk space can be released by running an initial sync. This involves stopping the mongod instance, emptying the data directory, and then restarting to allow it to reconstruct the data through replication.
Comments
Post a Comment