Array Data Structure, Javascript Array Object and Introduction to Dense and Sparse arrays.

In this story, I will cover the Array Data Structure and some interesting core facts about the Javascript Array Object that makes them different from the primitive array data structure in detail. To understand this story better, you should have a basic idea about arrays in javascript.
What is an array ?
“Array is a fixed size collection of homogeneous elements”. Array is one of the most simple data structures and probably, the most used data structure as well. Following are some of the features of array:
- Fixed size Array has a predefined fixed size.
- All the elements have same data type.
- Every element is assigned an index starting from 0 to n-1, where n is number of elements.
- Contiguous Memory Allocation Array is being allocated to continuous blocks of memory.
- O(1) Time Complexity for Insert and Random Access.
- O(n) Time Complexity for Delete and Search.

What is Array Object in Javascript ?
Arrays in Javascript are list-like global objects. Although, they work pretty much like a primitive array data structure but it is actually an API which is implemented using a Hash Table. Due to the use of Hash Table, arrays in javascript are more powerful as a structure.
- Arrays in javascript are dynamic in size, whether you define the size initially or not.
let arr = new Array()
let arr = new Array(10);
let arr = [];- An Array in javascript can have elements with different data types.
let arr = [1,'hello',true,undefined]- Javascript supports both dense and sparse arrays.
What are dense and sparse arrays ?
Dense Arrays are only allocated contiguous blocks of memory.
Sparse Arrays doesn’t necessarily have to be allocated contiguous blocks of memory .
Why javascript supports sparse arrays ?
The answer is simple it allows arrays to be dynamic in size and data types. But most importantly, it improves memory utilization.
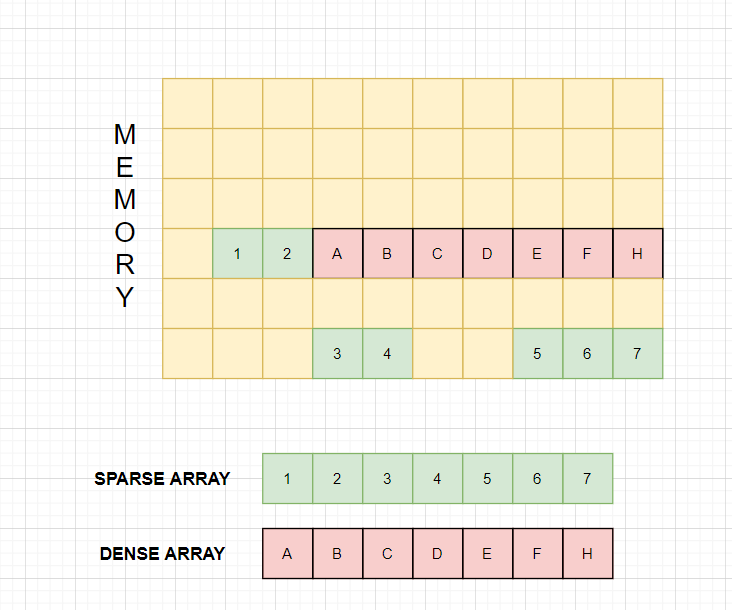
How to create a sparse array in javascript ?
Javascript tends to automatically create a sparse array if required in order to utilize the memory much efficiently. And javascript is doing this more often than you even notice. Consider the following example:
let arr = [1,2,3];
arr[50] = 50;We have defined an array ‘arr’ with elements 1,2,3. Javascript allocates a contiguous memory for ‘arr’ after reading the first statement. Then javascript reads the second statement and allocates the memory for that element in memory. But here is the thing, it will not allocate memory for index 3 to index 49. Instead it will just allocate memory for index 50. See the block diagram below :

By this time there are two very important questions that needs to be answered.
What is the value in index 3 to 49 ?
console.log(arr[3],arr[4],arr[49])
// output : undefined undefined undefinedconsole.log(arr.filter( a => a === undefined)
// output : []
If you try to check the value of any index from 3 to 49 of array ‘arr’, they all will be ‘undefined’. But, if you filter the array to only have ‘undefined’ values then the result will be an empty array. Because, in reality javascript never allocated memory to the index 3 to 49 as they were never declared.
What is the length of the array arr ?
Although the index 3 to 49 are empty and there are only 4 indexes with values. Still, the length of the array will be 51. Because, that’s how javascript manages the consistent indexes by making holes for non declared indexes.
console.log(arr.length)
// output : 51Array Objects in javascript are amazing structures. But, if you want to create a primitive array data structure in javascript you can do that using typed arrays in javascript. Try that and let me know in response section if you find something cool.




Comments
Post a Comment