What is Rsync?
For those wondering, Rsync is a fast, versatile file copying utility that can be used to copy and transfer files or folders to and from remote and local systems. It offers a large number of options that control every aspect of its behavior and permit very flexible specification of the set of files to be copied. It is famous for its delta-transfer algorithm, which reduces the amount of data sent over the network by sending only the differences between the source files and the existing files in the destination. Rsync is widely used for backups and mirroring and as an improved copy command for everyday use.
Just like SCP, rsync will also copy files over SSH. In case you wanted to download or transfer large size files and folders over SSH, I recommend you to use rsync utility as described below.
Resume Partially Transferred Files Using Rsync
Please that the rsync utility should be installed on both sides (i.e. remote and local systems) in order to resume partially transferred files. Rsync is available in the official repositories of most Linux distributions, so you can install it using the distribution’s default package manager.
On Arch Linux and its variants, install Rsync using command:
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
On Fedora:
On RHEL, CentOS:
On SUSE/openSUSE:
Now let us see an example. I am going to copy Ubuntu 18.04 ISO from my local system to remote system with command:
Here,
- sk is my remote system’s username
- 192.168.225.22 is the IP address of the remote machine.
- /home/sk/ is the remote destination.
Now, I terminated the copy process forcibly by pressing CTRL+C.
Sample output:
As you see in the above output, I terminated the copy process when it reached 33%.
If I re-run the above command, it will simply overwrite the existing file. In other words, the copy process will not resume where I left it off.
In order to resume the copy process to copy the partially transferred ISO file, use rsynccommand as shown below.
Sample output:
See? Now, the copying process is resumed where we left it off earlier.
You can also use “–partial” instead of parameter “-P” like below.
Here, the parameter “–partial” or “-P” tells the rsync command to keep the partial downloaded file and resume the process.
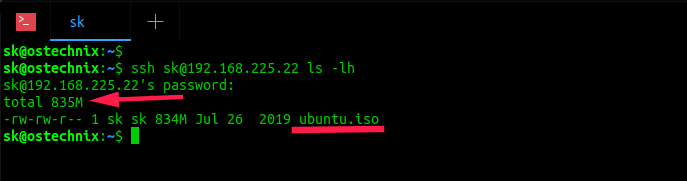
Check if the file is really copied or not to the remote system using command:
As you see in the above output, the file Ubuntu.iso is copied to the remote system and its size is 835MB.


Comments
Post a Comment