We will create a small and easy Angular application to check if user is connected to Internet or not with the use of Angular Material.
Create a Snackbar to check whether a user is online or offline in Angular in a minute! A small and easy Angular application to check if user is connected to Internet or not with use of Angular material
First of all you have to install a packaged called ng-connection-service. Lets see how do we do that.
Create new Angular application using CLI
_ng new Online_
Install the ng-connection-service package inside the application from the CLI using:
_npm install ng-connection-service — save_
Once if you done this process please check your package.json whether it is added or not
You should see something like below,
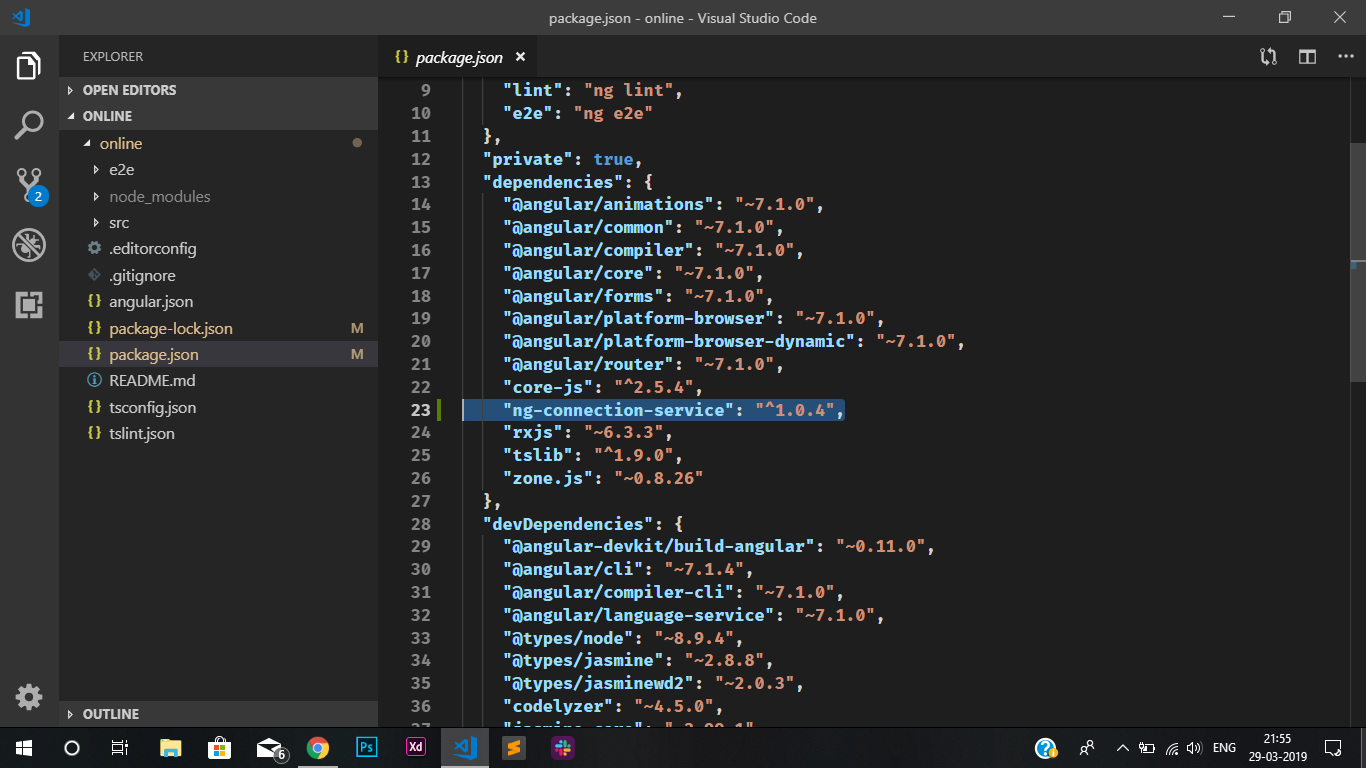
package.json
now, time to install Angular Material into your project using CLI
npm install — save @angular/material @angular/cdk @angular/animationsnow, import it in app.component.ts like below:
import {MatSnackBar,MatSnackBarConfig,MatSnackBarHorizontalPosition,MatSnackBarVerticalPosition} from ‘@angular/material’;Let us finally inject the service inside the component. If you are familiar with service, you’d know that to inject a service, we go to the constructor of the component class and inject it as follows:
constructor(private connectionService: ConnectionService, public snackbar: MatSnackBar){
});now the time for write logic of checking the internet connectivity. See the code below:
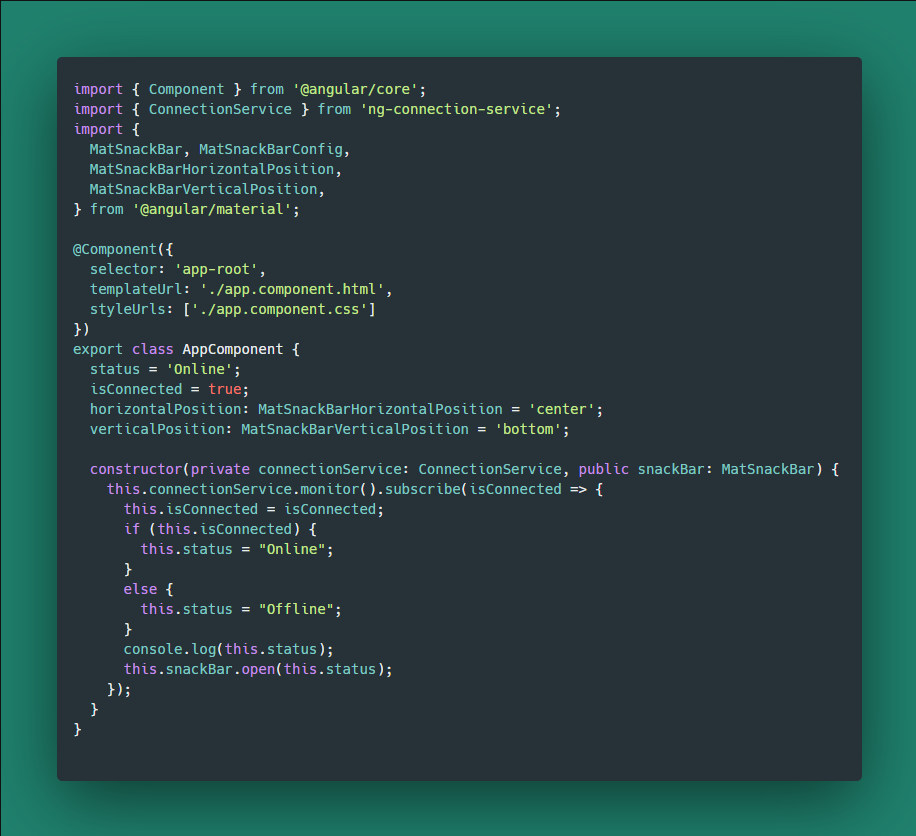
app.component.ts
Final result look like:

final output
Conclusion
Here you can see whenever I turned off my wifi connection Snackbar pop up in bottom and show OFFLINE Status. Thus in this article we have learnt how we can detect internet connection status in an Angular Application. Thank you for reading!
Comments
Post a Comment