Capacitor overview
First off, let’s go over what Capacitor is and how it relates to other cross platform projects out there.
At a glance, Capacitor follows many of the same ideas as Apache Cordova.
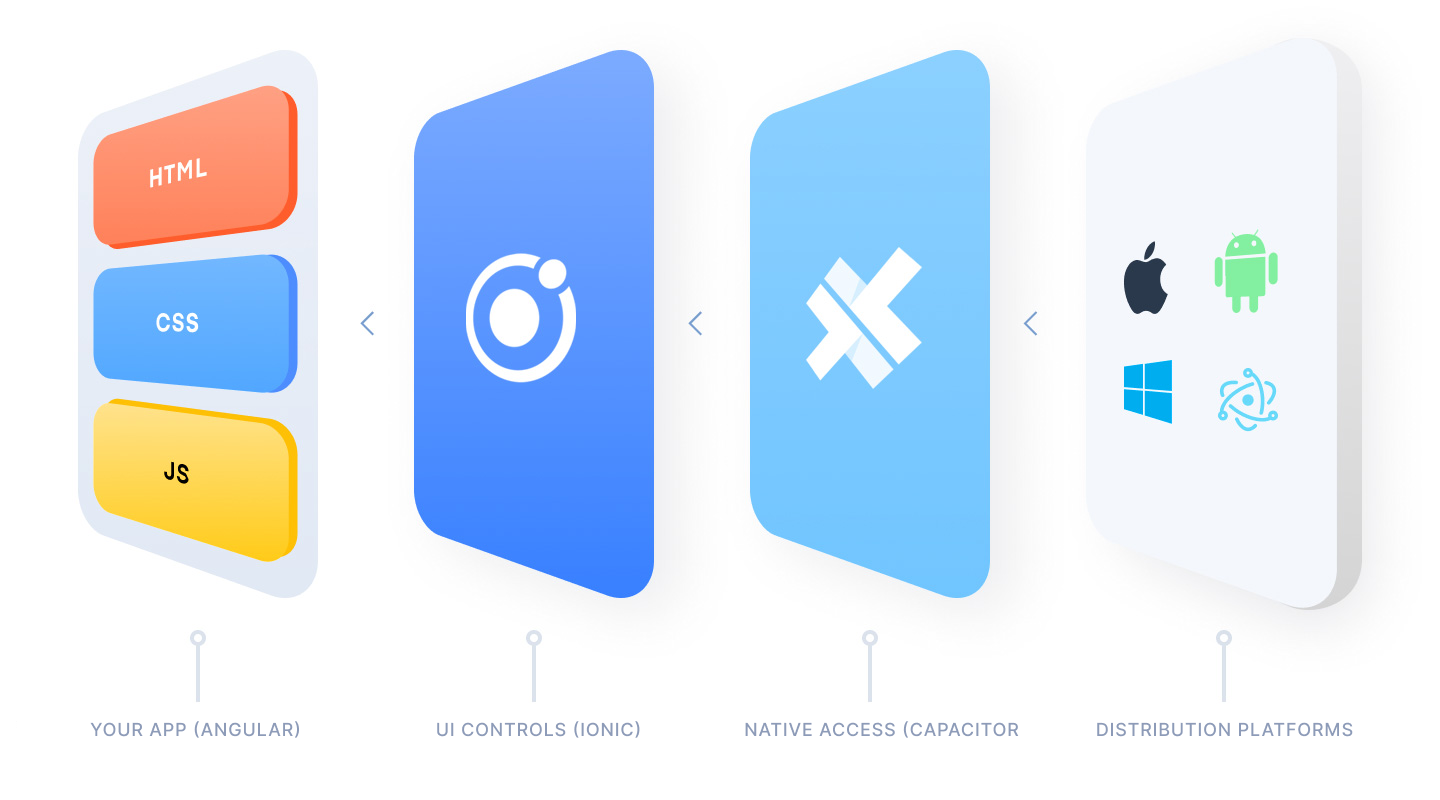
There is a Web layer that renders the app and a native layer that listens for calls to Native APIs. Within those layers are many technical decisions that make the overall developer and user experience much smoother.
- Unified API that makes cross-platform development easier
- Native Platforms are not distribution targets, but are committed to version control and can be edited by the developer.
- Modern native build tools and libraries, such as Cocoapods, Android Libraries, Xcode and Android Studio, provide more visibility into native project changes and better app maintainability.
- Utilize
npmand modern JS tooling to simplify adding core plugins and creating new ones.
These principles bring the best of web development and native development with little to no friction for developers.
Capacitor and Angular integration
Capacitor itself is made up of 2 packages, the core functionality (@capacitor/core) and the CLI (@capacitor/cli). To add Capacitor to your project, let’s start with a simple Angular App from the Angular CLI.
ng new capApp --routing --style css
cd capAppWith the app created, let’s add Capacitor to our project.
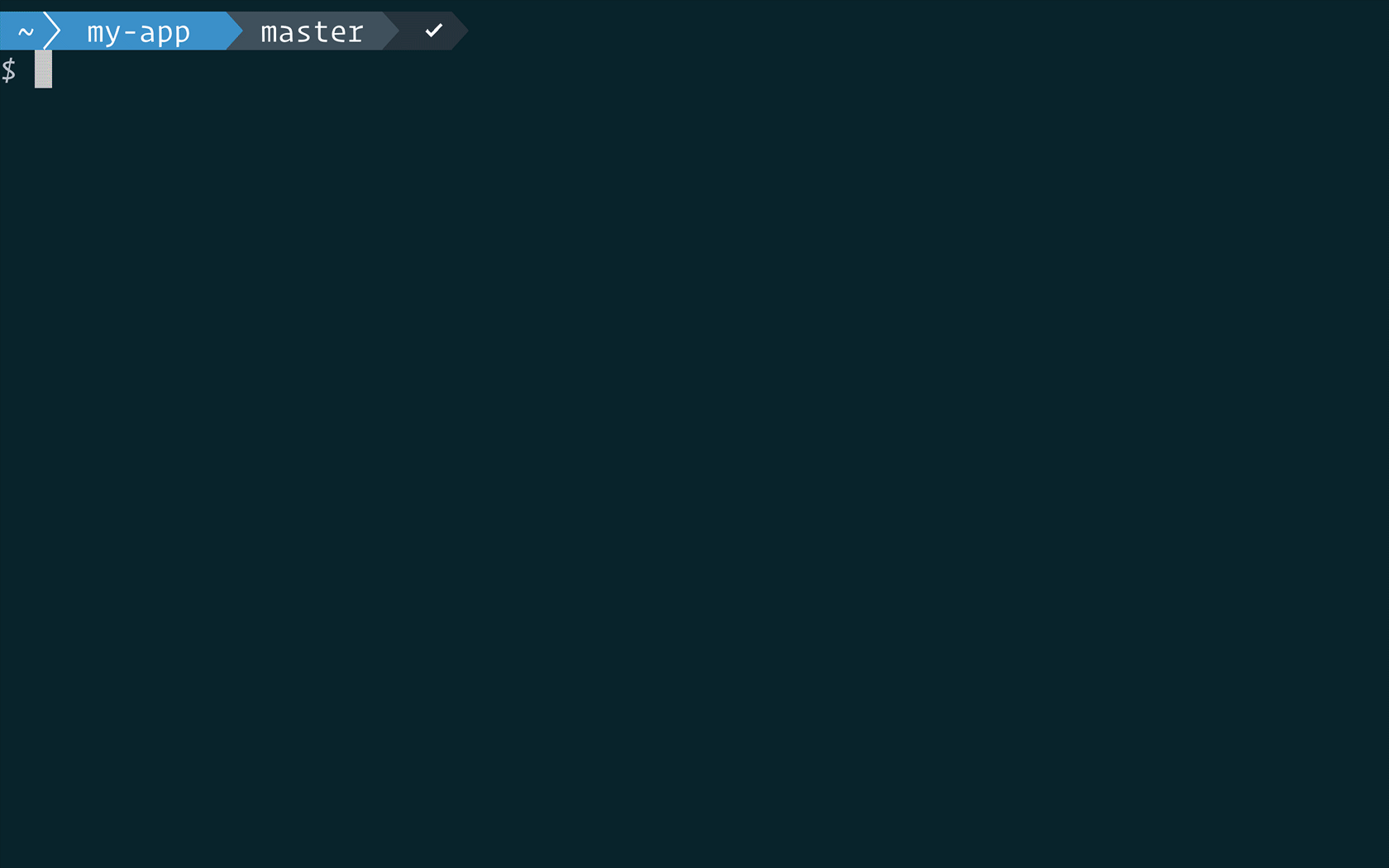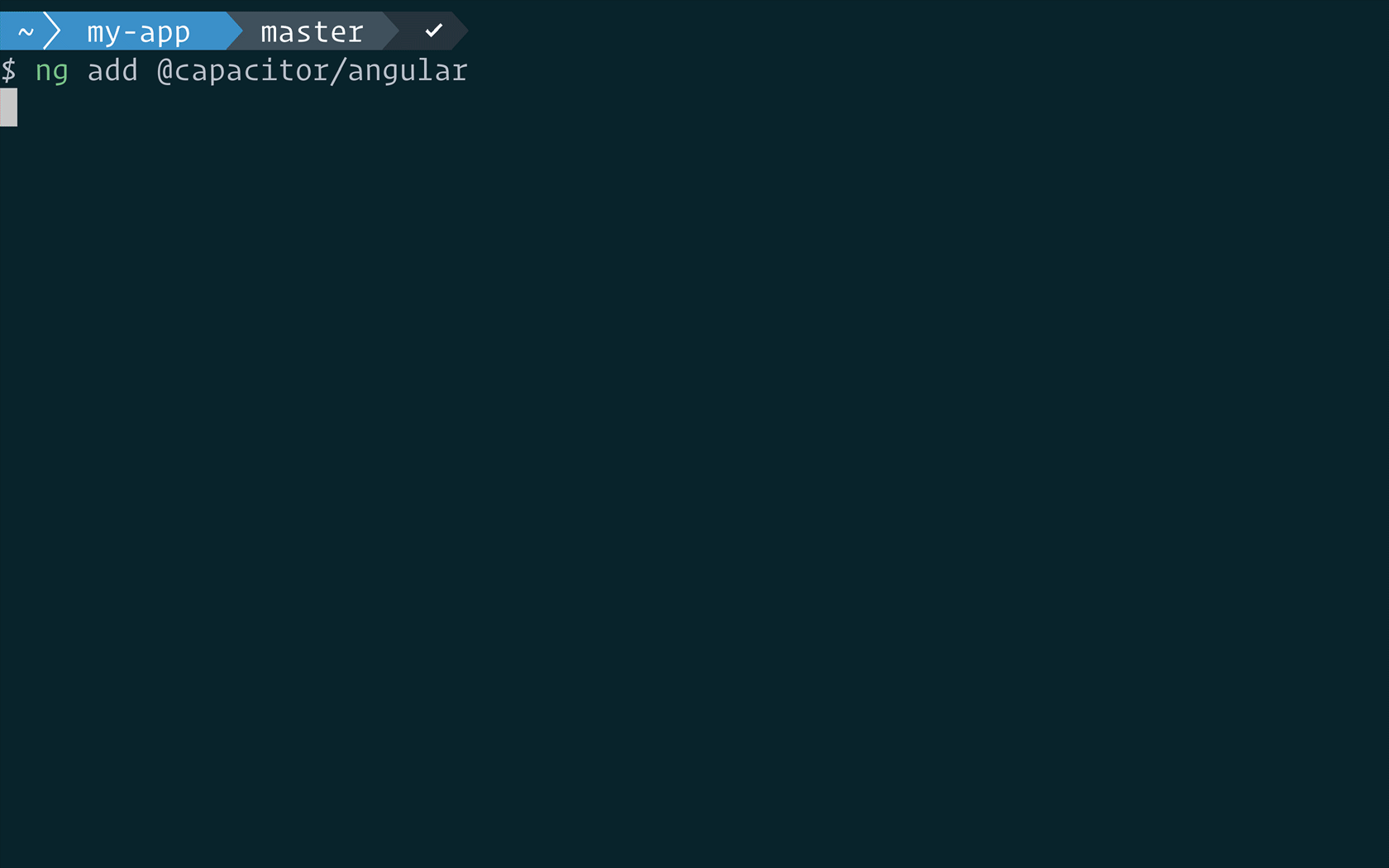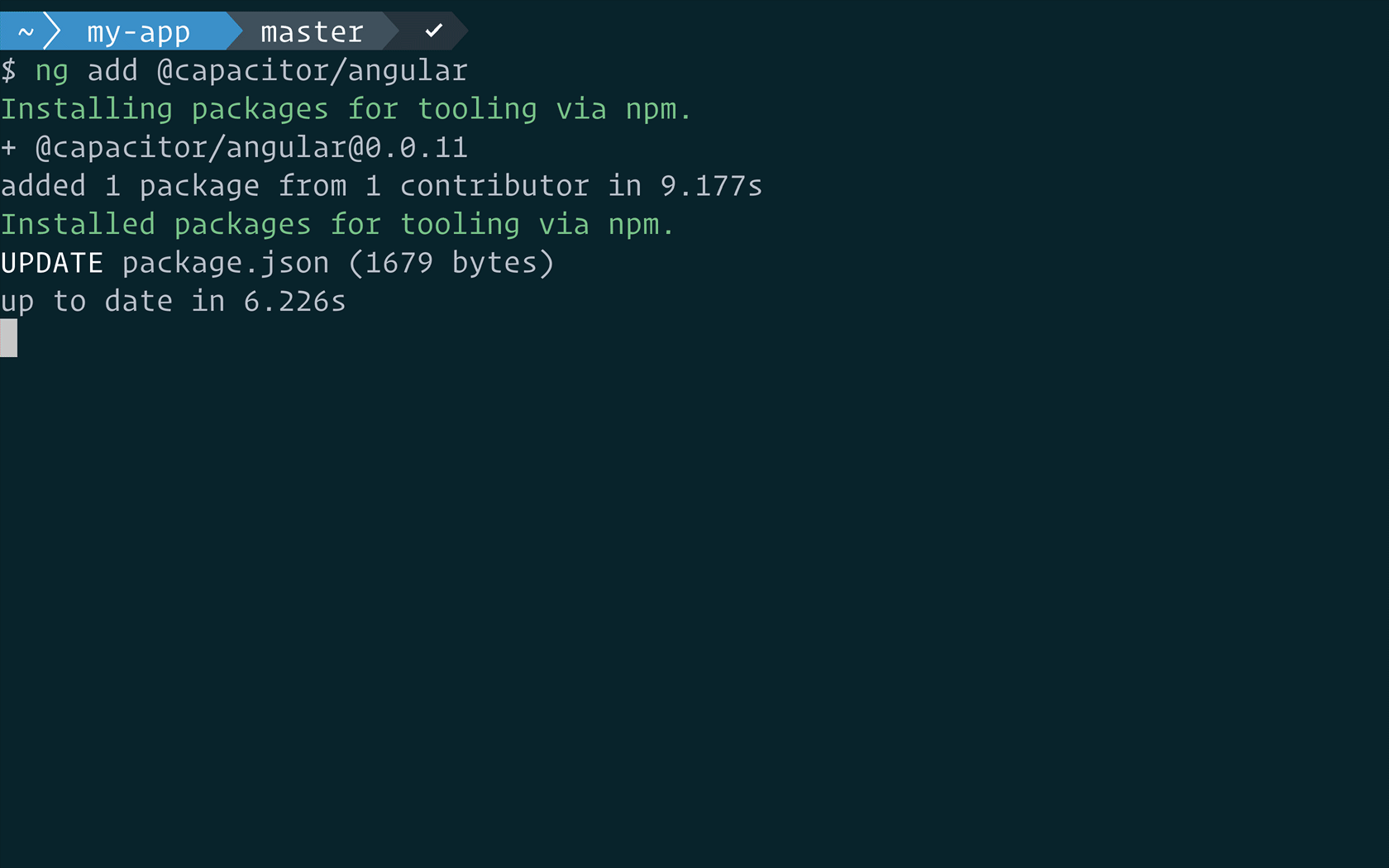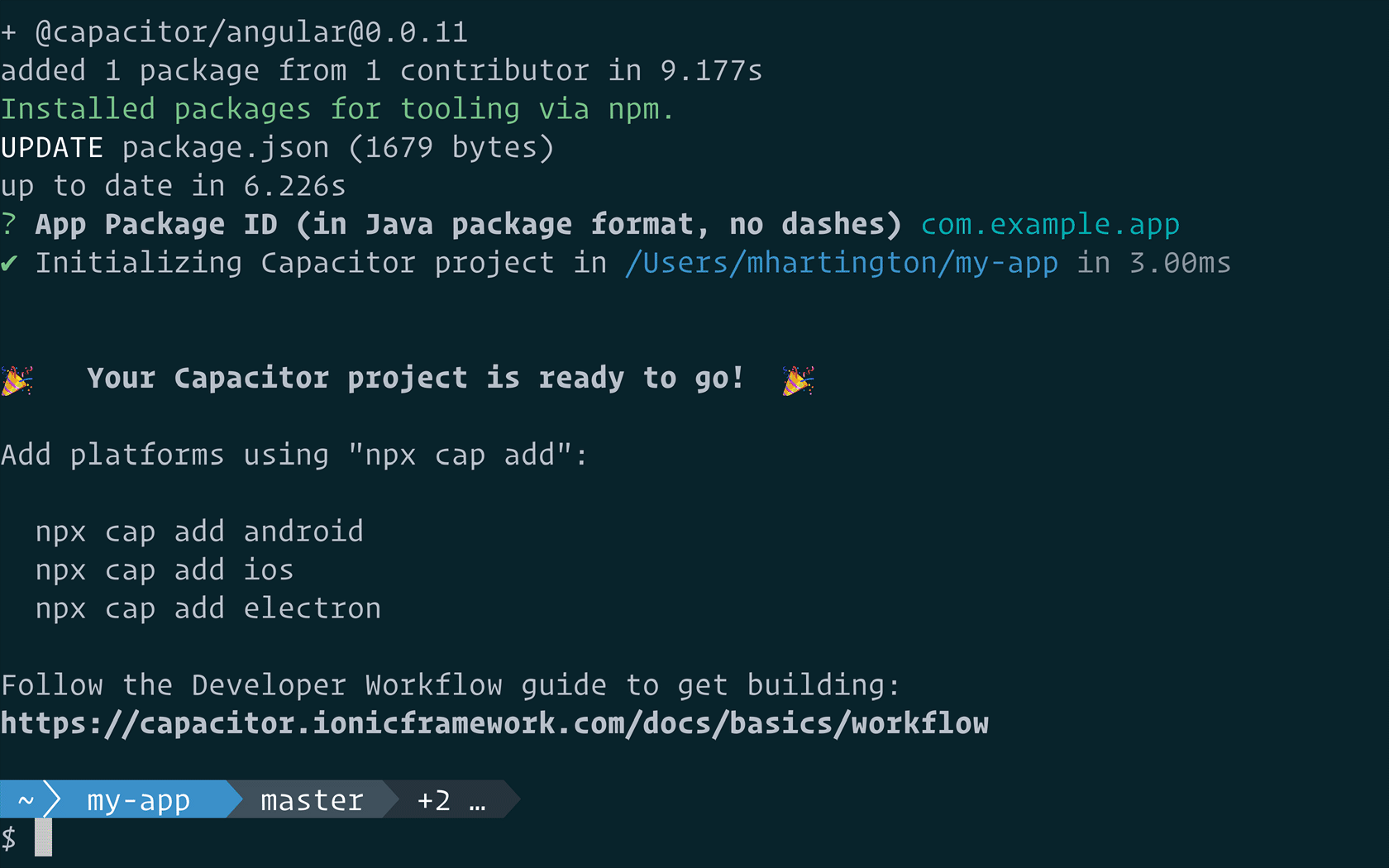
ng add @capacitor/angularWith this, developers can add Capacitor to their project with ease.

When the schematic is done running, developers should build our app, and run npx cap add <ios,android> or yarn cap add <ios, android> and our Xcode or Android Studio projects will be created!
ng run capApp:build
npx cap add iosPulling back the curtain
So what is the schematic actually doing behind the scenes?
- Installing Capacitor Dependencies
First, it adds Capacitor dependencies to the package.json: Core and CLI.
- Installs dependencies
This will just do a quick npm (or yarn) install then make sure we have the Core and CLI packages for Capacitor.
- Run Capacitor CLI’s init script and create the scaffolding needed.
To make sure that the Capacitor project understands your Angular project, the schematic infers a lot of data based on your angular.json. It will read your app's name and use that when creating the iOS and Android projects, as well as read the build folder so it knows where to copy your web code when preparing the native projects. This means that your Capacitor project will feel like a natural extension of your Angular project.
Once added, we do a build of our app, and deploy to either iOS, Android, web, or Electron. For building to iOS or Android, you’ll need to have the native SDKs and tools installed. For a detailed guide on this, see this guide for iOS and this guide for Android

Comments
Post a Comment