FormArray tracks the value and validity state of an array of FormControl, FormGroup or FormArray instances. To create a FormArraywe can pass an array of FormControl or FormGroup. A FormArray will be called validated only if its FormControl or FormGroup are validated. To provide a custom error messages on UI, we can fetch FormArray validation status in HTML template. On this page we will create a reactive form using
FormBuilder and then we will validate and submit the form.Technologies Used
Find the technologies being used in our example.1. Angular 8.0.3
2. TypeScript 3.4.3
3. Node.js 12.5.0
4. Angular CLI 8.0.6
FormArray Validation
We can pass following arguments to instantiateFormArray.1. First argument is array of controls such as
FormControl, FormGroup or FormArray. 2. Second argument is for sync validators. It is optional.
3. Third argument is for async validators. It is also optional.
Find the sample example.
We are using
Validators.required at FormArray level. It means the size of FormArray must be greater than zero.Output
Look into output, when there was no element in
FormArray then validity status was invalid and when we pushed a control then FormArraybecame valid.FormArray Validation using FormControl
SupposeFormArray is the array of FormControl. Then FormArray will not be considered validated if any of the FormControl is invalid. Find the code snippet.Find the output.
FormArray is containing two FormControl and they need to be validated and only when FormArray will be considered validated.FormArray Validation using FormGroup
SupposeFormArray contains the array of FormGroup and each FormGroup contains FormControl with some validators. FormArraywill be considered validated only if all the FormGroup are validated and FormGroup will be validated only if all the FormControl are validated. Find the code snippet.Find the output.
FormArray Validation Example with FormBuilder
We will create a reactive form usingFormBuilder which has methods such as group() to create FormGroup, control() to create FormControl and array() to create FormArray. In our example we will create
FormArray that will contain array of FormGroup and each FormGroup will contain some FormControl with validators. At run time we will push and remove controls from FormArray instance. Find the code snippet to create team form.
The
createEmpFormGroup() method is creating a FormGroup as following. This will add an employee in team.To access validation state of
FormArray and its elements, find the getter method for employeesform array control.Now in HTML template we can access
FormArray validation errors for custom error messages as following.In the above code
i is the index of employeesform array. Find the print screen of output of our example. When we try to submit the form without validations, we will get following error messages.
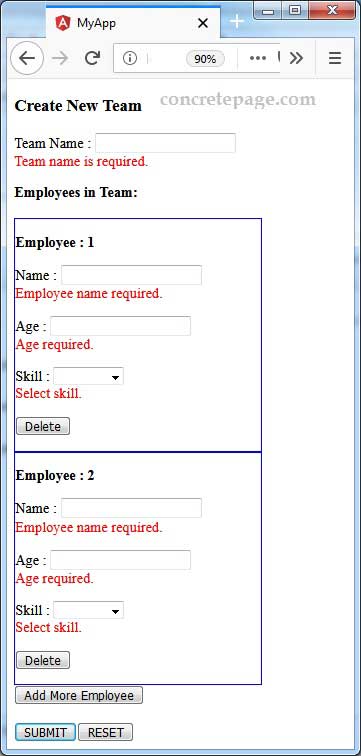
team-management.component.ts
team-management.component.html
employee.ts
team.ts
team-management.service.ts
app.component.ts
styles.css
app.module.ts
Comments
Post a Comment