Introduction
In a web application, we generally show a process status by graphical indicators like progress bars and spinners. In this post, we will discuss How To Add Loader/Spinner In Angular 8 Application, we will learn how we can show the Loader in Angular 8 using Ngx spinner library. Ngx spinner is a library for loading spinner for Angular, which is meant to inform the user that data loading is in progress. Basically Loader is used to show the loading state of data in application.
Prerequisites
- Basic Knowledge of Angular 2 or higher
- Visual Studio Code
- Visual studio and SQL Server Management studio
- Node and NPM installed
- Bootstrap
Step 1
Create an Angular project by using the following command.
ng new Angularloader Step 2
Open this project in Visual Studio Code and install bootstrap by using following command
npm install bootstrap --save Now open styles.css file and add Bootstrap file reference. To add reference in styles.css file add this line.
@import '~bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css'; Step 3
Now install ngx spinner library in this project, to install ngx spinner library use the following command
npm install ngx-spinner --save Step 4
Now Update app.module.ts
Open app.module.ts file and add Import NgxSpinnerModule in the root module,
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http'
import { EmployeedetailsComponent } from './employeedetails/employeedetails.component';
import { NgxSpinnerModule } from "ngx-spinner";
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
EmployeedetailsComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule,
HttpClientModule,
NgxSpinnerModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { } Step 5
Now create a new component by using the following command.
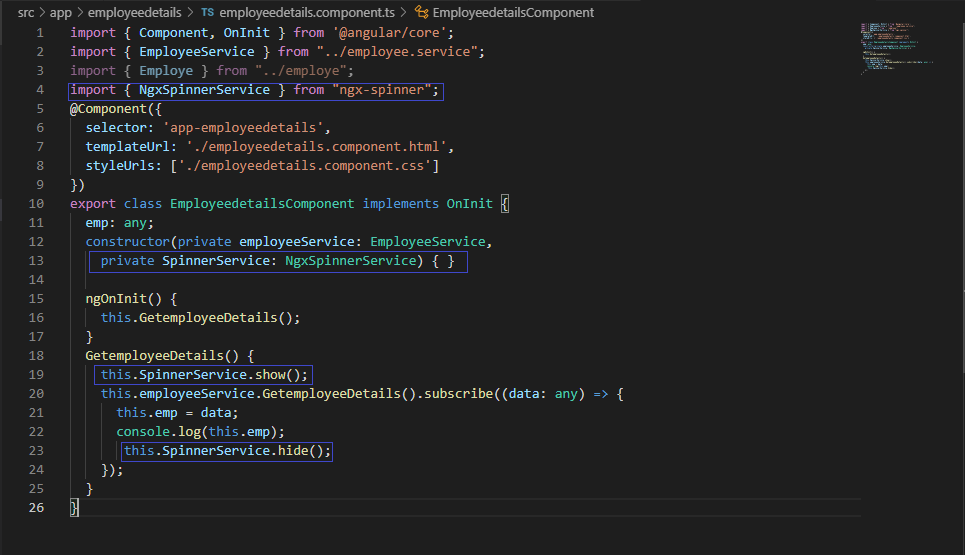
ng g c Employeedetails --spec=false Now open employeedetails.component.ts file and import NgxSpinnerService
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { EmployeeService } from "../employee.service";
import { Employe } from "../employe";
import { NgxSpinnerService } from "ngx-spinner";
@Component({
selector: 'app-employeedetails',
templateUrl: './employeedetails.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./employeedetails.component.css']
})
export class EmployeedetailsComponent implements OnInit {
emp: any;
constructor(private employeeService: EmployeeService,
private SpinnerService: NgxSpinnerService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.GetemployeeDetails();
}
GetemployeeDetails() {
this.SpinnerService.show();
this.employeeService.GetemployeeDetails().subscribe((data: any) => {
this.emp = data;
console.log(this.emp);
this.SpinnerService.hide();
});
}
} Open employeedetails.component.html file and following lines
<div>
<div class="row" style="margin-top:10px;margin-bottom: 10px;">
<div class="col-sm-12 btn btn-success">
Loader in Angular Application with Dynamic Data
</div>
</div>
<div class="row" style="margin-top:10px;margin-bottom: 10px;">
</div>
</div>
<hr style="background-color:black" />
<div>
<table class="table table-dark table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Address</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>ContactNum</th>
<th>Salary</th>
<th>Department</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor="let e of emp">
<td>{{e.Id}}</td>
<td>{{e.Name}}</td>
<td>{{e.Age}}</td>
<td>{{e.Address}}</td>
<td>{{e.City}}</td>
<td>{{e.ContactNum}}</td>
<td>{{e.Salary}}</td>
<td>{{e.Department}}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<ngx-spinner bdColor="rgba(51, 51, 51, 0.8)" size="default" type="ball-spin-clockwise">
<p style="color: white">Please Wait. </p>
</ngx-spinner> Step 6
Create a new class using following command,
ng g class Employe --spec=false Now open employe.ts file and add the following line in this class
export class Employe {
Id:number;
Name:any;
Age:any;
Address:any;
City:any;
ContactNum:number;
Salary:number;
Department:any;
} Step 7
Create a new service using following command
ng g s Employee --spec=false Now open employee.service.ts file and add following lines
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient } from "@angular/common/http";
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class EmployeeService {
url:any;
constructor(private http:HttpClient ) {
}
GetemployeeDetails()
{
this.url='http://localhost:56932/api/Employee/Employeedetails';
return this.http.get(this.url);
}
} *Step 8 - Create database and a table *
Open SQL Server Management Studio, create a database named "Employee", and in this database, create a table. Give that table a name like "employee".
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Employee](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Name] [varchar](50) NULL,
[Age] [int] NULL,
[Address] [varchar](50) NULL,
[City] [varchar](50) NULL,
[ContactNum] [varchar](50) NULL,
[Salary] [decimal](18, 0) NULL,
[Department] [varchar](50) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Employee] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
GO 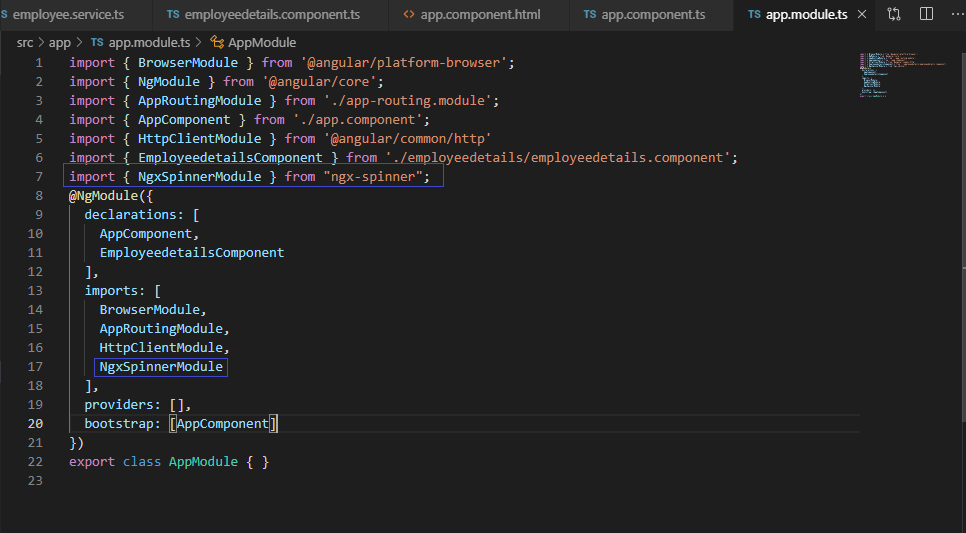
Comments
Post a Comment