All we use forms in our applications. Selects in Forms are great when you have multiple options. In Angular as a OPTION value we can use not only string literals, but also objects.
Simplest SELECT
<form [formGroup]="countryForm">
<select formControlName="countryControl">
<option [value]="country" *ngFor="let country of countries"> {{country}}</option>
</select>
</form>
And in .ts file
countryForm: FormGroup;countries = ['USA', 'Canada', 'Uk'] constructor(private fb: FormBuilder) {}ngOnInit() { this.countryForm = this.fb.group({ countryControl: ['Canada'] }); }
After this we will have our SELECT with ‘Canada’ selected as default

That all is good, but what about having complex object as OPTION value, rather than a regular string. For that Angular provides [ngValue] directive.
Now let’s modify our countries array so instead of strings it will contain objects with country name, country currency code and unique property (id in this case)
countries = [{
id: '8f8c6e98',
name: 'USA',
code: 'USD'
},
{
id: '169fee1a',
name: 'Canada',
code: 'CAD'
},
{
id: '3953154c',
name: 'UK',
code: 'GBP'
}]
Now as country is an object, in our template we need to display country.name for SELECT OPTIONS and also use [ngValue] directive as we are passing an object as a value.
<option [ngValue]="country" *ngFor="let country of countries">{{country.name}}</option>
Also to provide a default value we need to set one of objects from countries array.
this.countryForm = this.fb.group({
countryControl: [this.countries[1]]
});
So now we have the same SELECT but now as a value we get not the name of the country, but whole country object.
Now let’s assume that we need to add an input where users can add more OPTIONS for this SELECT. We will have two inputs where users can add country name and country code. After that new OPTION will be added to our SELECT and that OPTION automatically will be selected. So usually all OPTIONS from SELECT come from the server, so in a real world example you also need to add new OPTIONS to the server, do a POST request and get brand new data. In this example i will simulate it with setTimeout.
So in template file
<input type="text" #name placeholder="Add country name">
<input type="text" #code placeholder="Add country code">
<button (click)="addNewOption(name.value, code.value)">Add to SELECT</button>
Add
addNewOption() method in .ts fileaddNewOption(name: string, code: string) { setTimeout(() => { this.countries = [ { id: '8f8c6e98', name: 'USA', code: 'USD' }, { id: '169fee1a', name: 'Canada', code: 'CAD' }, { id: '3953154c', name: 'UK', code: 'GBP' }, { id: '68c61e29', name, code } ];this.countryForm.controls['countryControl'].patchValue( {id : '68c61e29', name, code} ) }, 500) }
So here we are getting values from two inputs and simulating call to server. As a result we are getting a new data containing countries (included one that we added) and assigning to countries array (ID was generated on ‘server’). After data was received we also use patchValue method to change the default value of our SELECT.
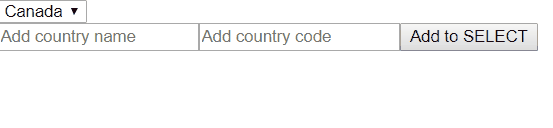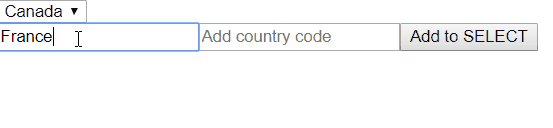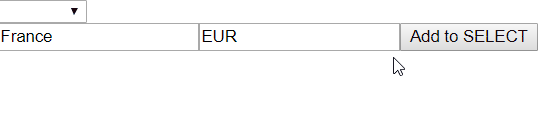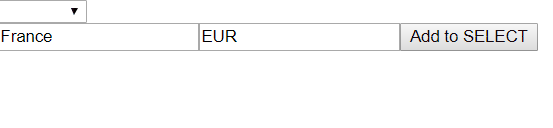
This is what will happen

So after submitting a new OPTION, it is there, but not selected. The reason of this is that Angular uses object identity to select options. So when we get a new data, objects will have different identities. Even that there is an object we provided in patchValue
{id : '68c61e29', name, code}
This object is not the same for Angular as the one that is inside countries array.
To solve this problem Angular provides compareWith input from SelectMultipleControlValueAccessor directive which is applied to our SELECT .
compareWithtakes a function which has two arguments:option1andoption2. IfcompareWithis given, Angular selects options by the return value of the function.
So first of all let’s write that function. Create a new function in .ts file
compareFn(c1: any, c2:any): boolean {
return c1 && c2 ? c1.id === c2.id : c1 === c2;
}
And add this function to SELECT
<select formControlName="countryControl" [compareWith]="compareFn">
...
After this Angular will compare OPTIONS using their ids rather than object identifiers. As a final result we got what we expected



Comments
Post a Comment